Primers • Convolutional Neural Networks
Overview
Summary
- CNN (Convolutional Neural Network) is a deep learning model designed for processing visual data. It uses convolutional layers to learn hierarchical representations and extract meaningful features from images. Here are the constituent layers from input to output in a typical CNN architecture:
- Image Input: An image is represented as a matrix of pixel values, with each pixel having 3 values (Red, Green, Blue), ranging from 0 (black) to 255 (white).
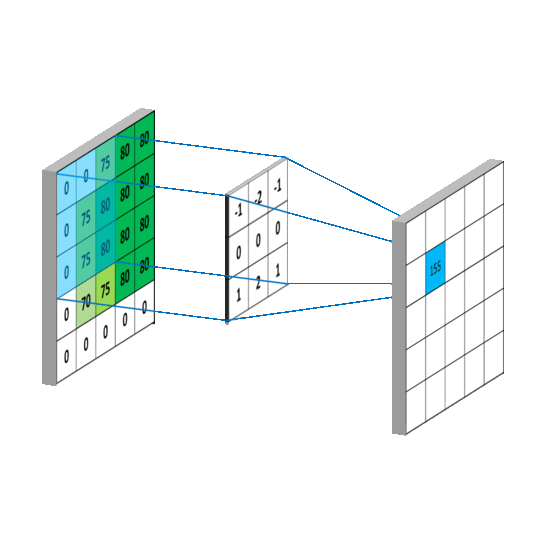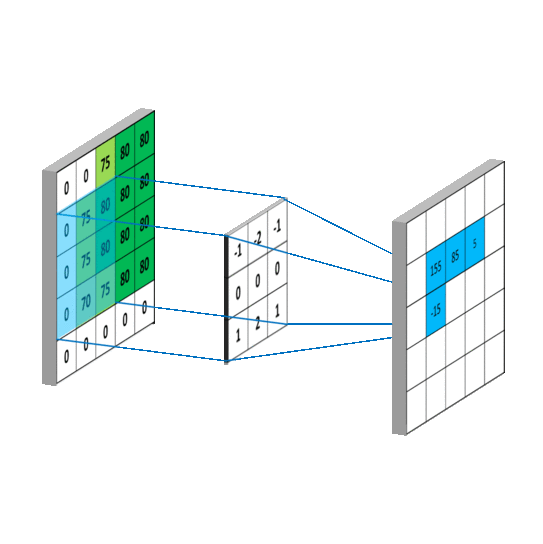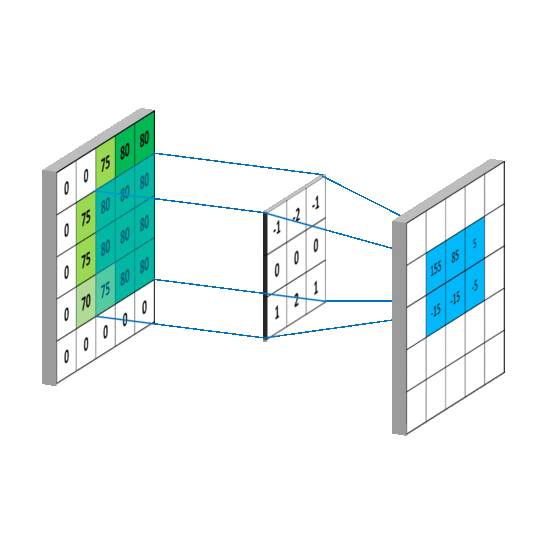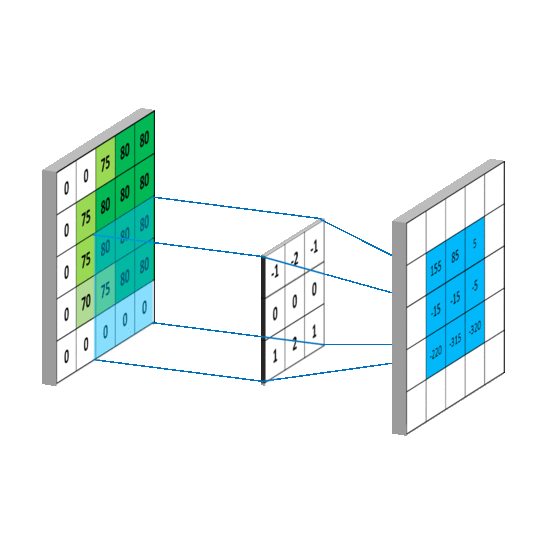
- Convolutional Layers: Convolutional layers apply filters or kernels to the input image, creating feature maps that identify important features like edges, lines, and textures.
- ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit): The ReLU layer applies the non-linear function max(0, x) to all inputs, increasing the CNN model’s non-linearity.
- Pooling Layers: Pooling layers reduce feature map dimensionality while retaining essential information. Max pooling selects the maximum value from the filter-covered section of the image.
- Fully Connected Layers: Fully connected layers enable high-level reasoning as neurons connect to all activations in the previous layer.
- Output Layer: The final layer uses softmax and sigmoid functions to output class probabilities. Softmax for multi-class, sigmoid for binary classification.
- Classification Result: The class with the highest probability is the CNN’s final prediction for the input image.
- CNNs learn hierarchical patterns, achieving impressive accuracy in image classification tasks
References
Citation
If you found our work useful, please cite it as:
@article{Chadha2020DistilledCNNs,
title = {Convolutional Neural Networks},
author = {Chadha, Aman},
journal = {Distilled AI},
year = {2020},
note = {\url{https://aman.ai}}
}