Overview
- The monitoring of machine learning models refers to the ways we track and understand our model performance in production from both a data science and operational perspective. Inadequate monitoring can lead to incorrect models left unchecked in production, stale models that stop adding business value, or subtle bugs in models that appear over time and never get caught. When ML is at the core of your business, a failure to catch these sorts of bugs can be a bankruptcy-inducing event - particularly if your company operates in a regulated environment.
- Martin Fowler has popularized the concept of Continuous Delivery for Machine Learning (CD4ML), and the diagram below (source) for this concept offers a useful visual guide to the ML lifecycle and where monitoring comes into play:
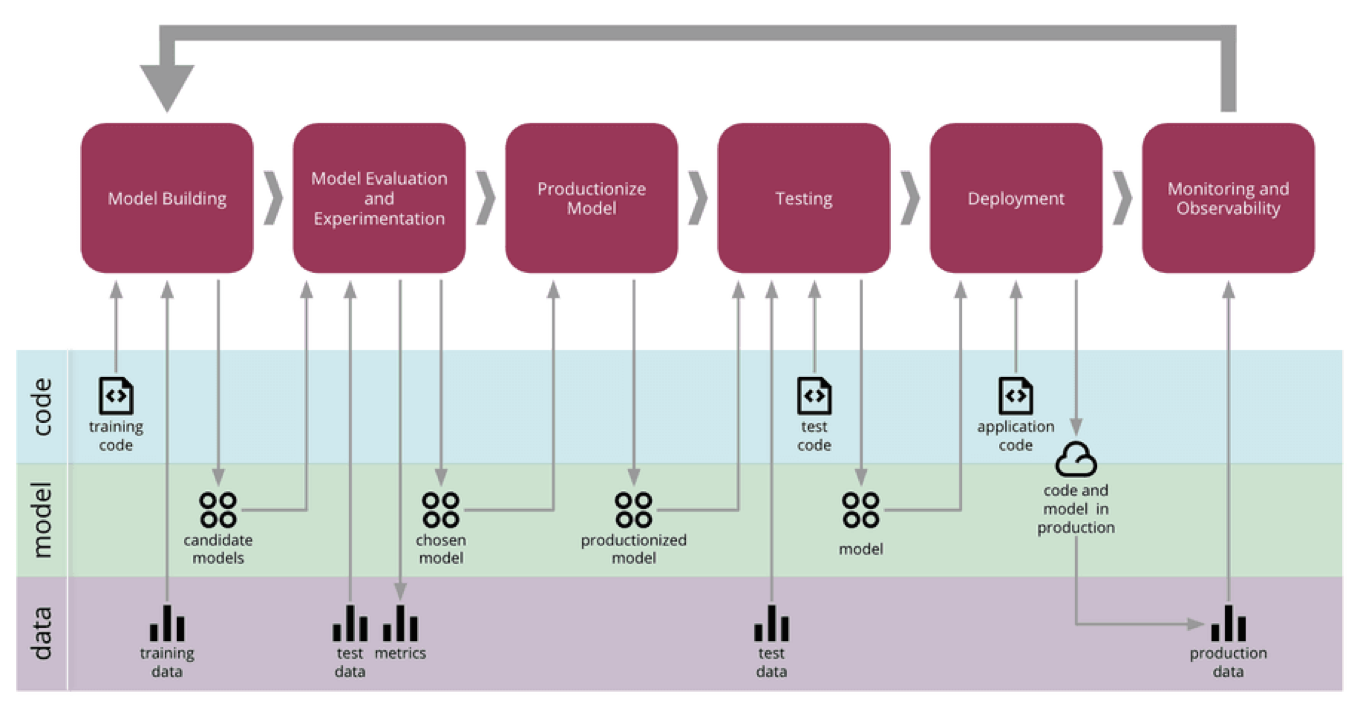
- LLM Ops refers to the set of best practices, tools, and techniques for managing and deploying LLMs in production. The image below (source) shows the LLMOps architecture in detail.
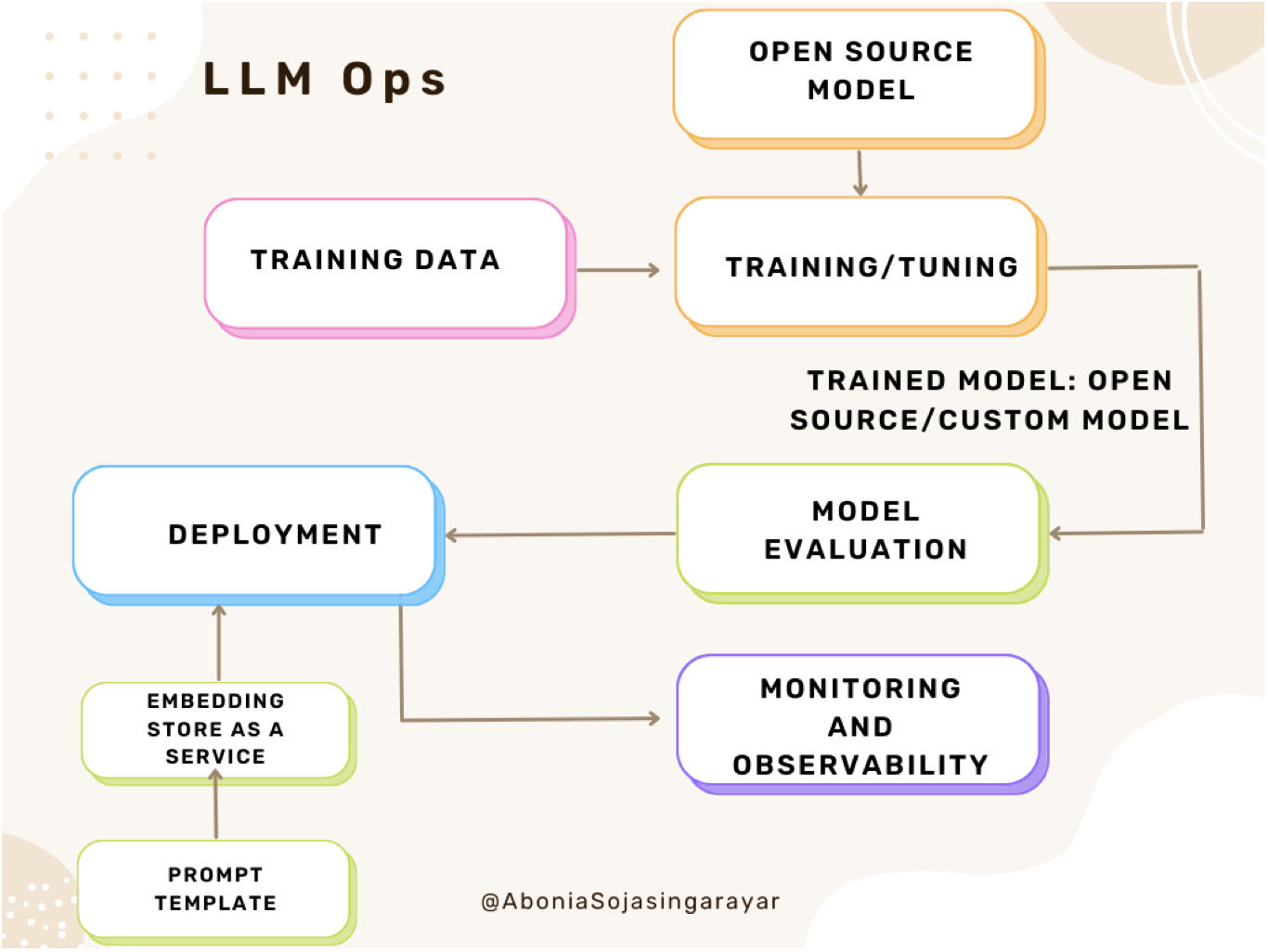
- It involves a range of tasks, such as data preprocessing, model training, model management, deployment, and monitoring. LLM Ops poses several challenges due to the large size and complexity of LLMs, as well as the need to ensure reliability, security, and interpretability and we’ll talk more about it below.
- This post is written in collaboration with Abonia Sojasingarayar, feel free to check out her page!
Best Practices for LLM Training
- Let’s start off by talking about some of the best practices for LLM training by looking at the key aspects we should look out for.
- Choosing the right hardware for training LLMs: LLMs require significant compute resources to train, and choosing the right hardware can have a big impact on the training time and cost. GPUs, TPUs, and cloud-based computing are common choices for LLM training.
- Preprocessing data and optimizing training data pipeline: Data preprocessing is an important step in LLM training, as it can affect the quality and performance of the model. Preprocessing techniques such as tokenization, normalization, and cleaning can improve the quality of the training data. Optimizing the training data pipeline can also speed up the training process and reduce costs.
- Selecting the right training algorithm and hyperparameters: LLMs can be trained using a variety of algorithms, such as LSTM, Transformer, and BERT, each with its strengths and weaknesses. Selecting the right algorithm and hyperparameters is critical for achieving good performance and avoiding overfitting or underfitting.
- Monitoring and tracking LLM training progress: Monitoring the training progress is important to ensure that the model is converging and not getting stuck in local minima. Tracking metrics such as loss, accuracy, and perplexity can help identify issues early and improve the training process.
Managing LLM Models
- Now we will delve a bit deeper into the best practices of managing large language models from saving and loading, to versioning, to reproducibility.
- Saving and loading LLM models: Saving and loading LLM models is an important part of model management, as it enables reuse of models and reduces the need for retraining. Formats such as TensorFlow SavedModel and ONNX are commonly used for saving LLM models.
- Versioning and managing LLM models: Versioning LLM models is critical for tracking changes and maintaining reproducibility. Tools such as Git and MLFlow can help with versioning and managing LLM models.
- Ensuring reproducibility of LLM models: Reproducibility is important for scientific and business applications of LLMs. Techniques such as containerization, virtualization, and reproducible pipelines can help ensure reproducibility of LLM models.
Deployment of LLM
- Choosing the right infrastructure for deploying LLMs: Deploying LLMs requires a reliable and scalable infrastructure that can handle the computational demands of LLM inference. Cloud-based solutions such as AWS, GCP, and Azure are popular choices for deploying LLMs.
- Scaling LLM deployments: Scaling LLM deployments involves distributing the load across multiple servers or nodes to handle high traffic and ensure low latency. Techniques such as load balancing, auto-scaling, and sharding can help with scaling LLM deployments.
- Managing and monitoring LLM deployments: Managing and monitoring LLM deployments is critical to ensure reliability, security, and performance. Techniques such as containerization, Kubernetes, and monitoring tools such as Prometheus and Grafana can help with managing and monitoring LLM deployments.
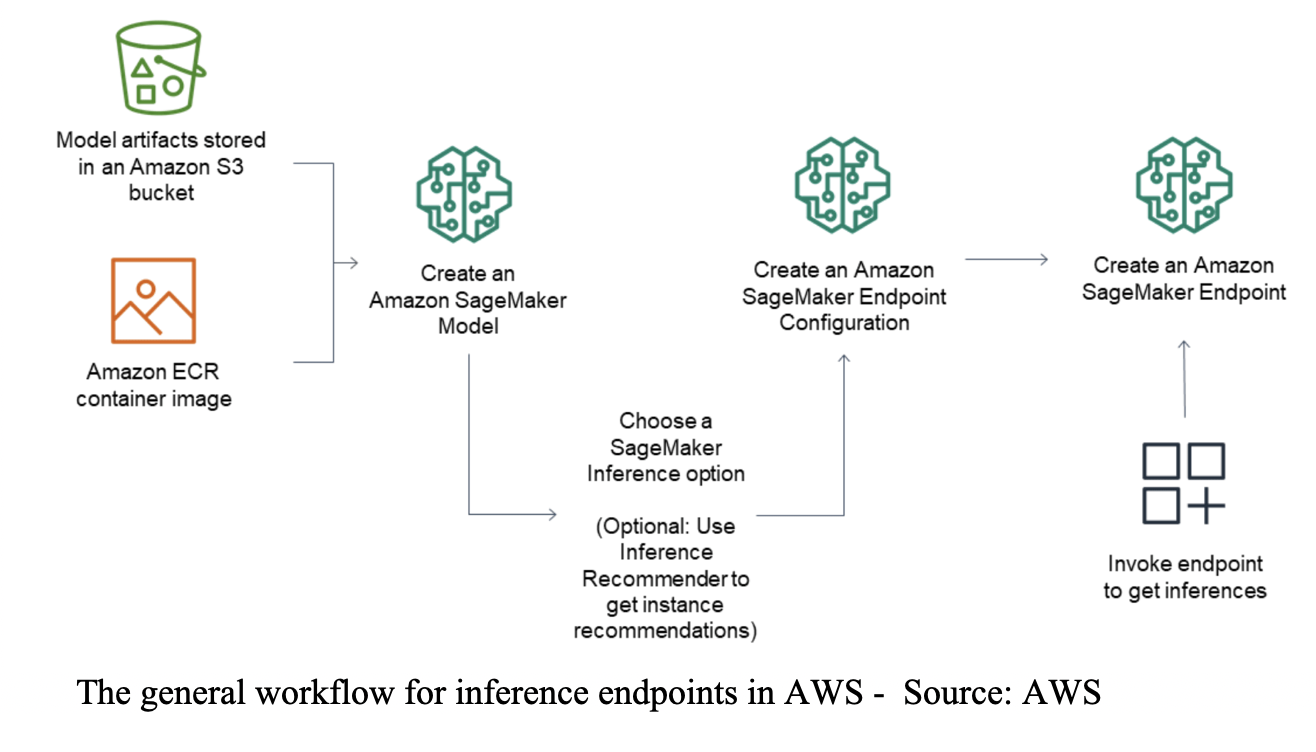
- The architecture below, (source) shows the general workflow for inference endpoints.
Security Considerations for LLMs
- LLMs pose unique security challenges due to their size, complexity, and sensitive data processing capabilities. To ensure the security of LLM models and data, MLOps engineers need to consider the following:
- Securing LLM models and data: This involves implementing access controls, encryption, and secure data storage to prevent unauthorized access to LLM models and data.
- Auditing LLM usage: It’s important to keep track of who is accessing LLM models and data, and for what purposes. This helps detect and prevent unauthorized usage or misuse of LLMs.
- Managing access to LLM models: MLOps engineers need to ensure that only authorized users and applications can access LLM models. This involves setting up authentication and authorization mechanisms, as well as implementing firewalls and network segmentation.
Interpretability and Explainability of LLMs
- LLMs are often considered “black boxes” because of their complexity and lack of transparency.
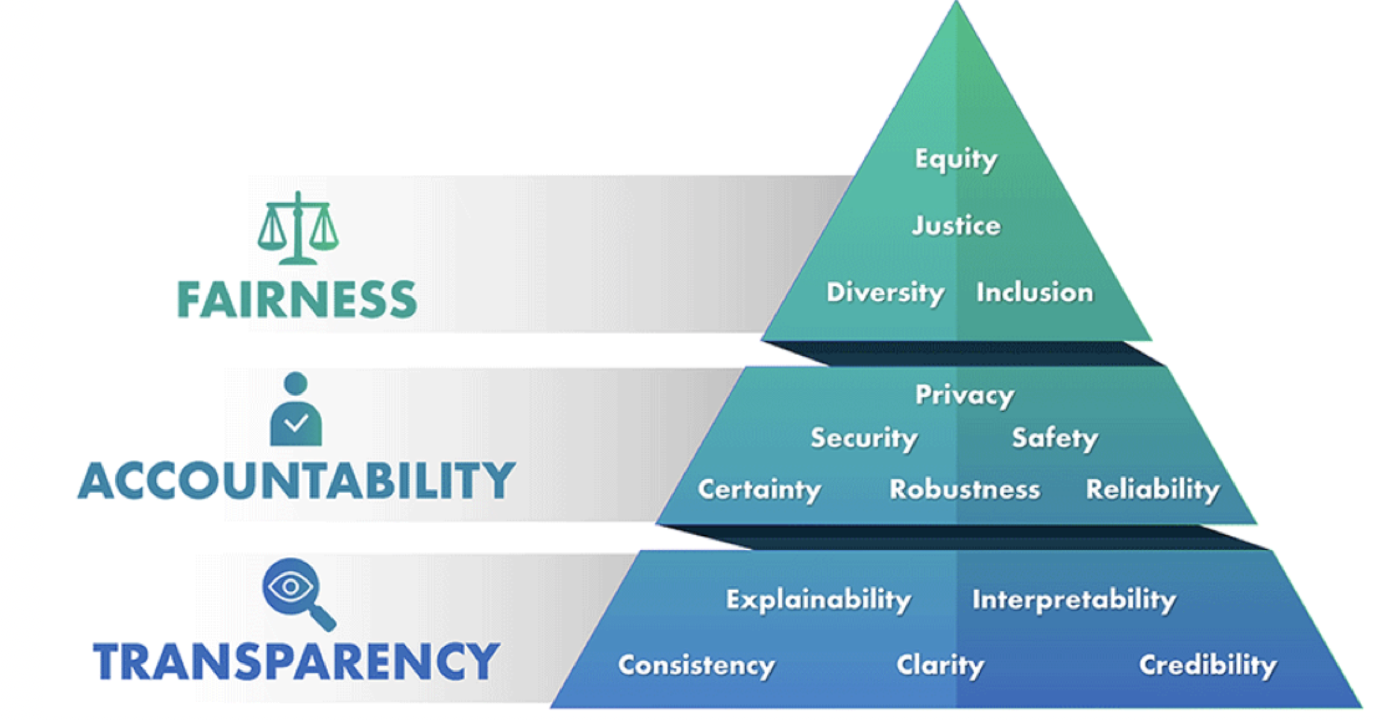
- However, interpretability and explainability are essential for ensuring trust and accountability in LLM models. To achieve interpretability and explainability, MLOps engineers can consider the following tenets shown in the image below (source):
- Understanding how LLMs make decisions: MLOps engineers need to understand the inner workings of LLM models to interpret their outputs and explain their decisions to stakeholders.
- Interpreting and explaining LLM model outputs: This involves using techniques such as feature importance analysis, attribution methods, and visualizations to understand how LLM models make predictions.
- Using interpretability tools to analyze LLM models: MLOps engineers can leverage interpretability tools such as LIME, SHAP, and Integrated Gradients to analyze LLM models and identify areas for improvement.
Fine-tuning LLMs
- LLMs can be fine-tuned for specific tasks by training them on task-specific datasets. Fine-tuning allows MLOps engineers to leverage the knowledge and parameters learned by pre-trained LLM models for specific applications. To fine-tune LLMs, MLOps engineers can consider the following:
- Fine-tuning pre-trained LLMs for specific tasks: This involves selecting the right pre-trained LLM model and fine-tuning it for specific tasks using task-specific datasets.
- Choosing the right fine-tuning approach and hyperparameters: MLOps engineers need to experiment with different fine-tuning approaches and hyperparameters to achieve the best results.
- Evaluating fine-tuned LLM models: MLOps engineers need to evaluate the performance of fine-tuned LLM models using appropriate metrics and validation techniques.
Optimization Techniques for LLMs
- LLMs can be computationally expensive and resource-intensive, which can limit their scalability and deployment in production environments. To optimize LLMs, MLOps engineers can consider the following:
- Compressing LLM models: This involves reducing the size of LLM models without compromising their performance by using techniques such as pruning, quantization, and knowledge distillation.
- Quantizing LLM models: This involves converting LLM models from floating-point to fixed-point arithmetic to reduce their memory footprint and improve their inference time.
- Using knowledge distillation for LLMs: This involves training a smaller, simpler model (the student) to mimic the behavior of a larger, more complex model (the teacher).
LLMs in Production
- Continuous Integration and Delivery (CI/CD): Deploying LLM models in production environments requires careful management of software development pipelines, version control, and testing. To enable continuous integration and delivery for LLM models, MLOps engineers can consider the following from (source):
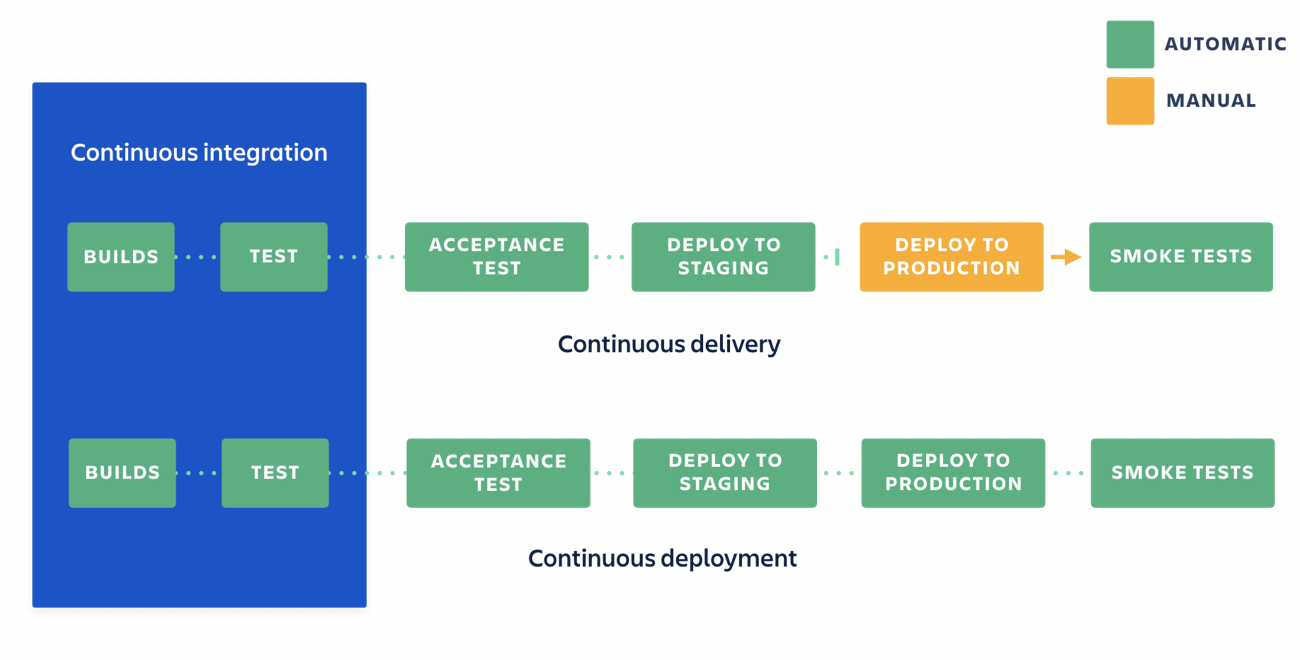
- Integrating LLM models into existing workflows: This involves integrating LLM models into existing software development workflows, such as Git-based version control systems and continuous integration platforms.
- Automating Integration and Delivery (CI/CD) of LLMs is an essential part of the overall LLM Ops workflow. In order to ensure that LLM models are deployed efficiently and effectively, it is important to integrate them into existing workflows and automate deployment pipelines. This allows for the continuous delivery of new LLM models and updates to existing ones, ensuring that they are always up-to-date and performing optimally.
- To integrate LLM models into existing workflows, it is important to have a clear understanding of the dependencies and requirements of the LLM models, as well as the existing infrastructure and systems in place. This can involve working closely with IT teams and DevOps engineers to ensure that LLM models can be deployed seamlessly and securely.
- Automating deployment pipelines is another important aspect of CI/CD for LLMs. This involves using tools and technologies such as Jenkins, Travis CI, or GitLab CI/CD to automate the process of building, testing, and deploying LLM models. This can help to reduce errors and ensure that LLM models are deployed quickly and consistently across different environments.
- Managing versioning and rollbacks of LLM models is also critical to ensure that LLM models are always performing as expected. This involves using version control systems such as Git to keep track of changes to LLM models and roll back to previous versions if necessary. It also involves using monitoring and logging tools to track the performance of LLM models in production and identify issues quickly.
- Overall, CI/CD is a critical part of LLM Ops, as it ensures that LLM models are deployed quickly and efficiently and that they are always up-to-date and performing optimally. By integrating LLM models into existing workflows, automating deployment pipelines, and managing versioning and rollbacks, teams can ensure that their LLM models are deployed securely and reliably.
Future of LLM Ops: Advancements and Challenges
- LLM Ops is a constantly evolving field with new trends and advancements. Keeping up with emerging research and development is essential for staying relevant and competitive. Some emerging trends include:
- AutoML: AutoML tools can automate several aspects of LLM development, from data preprocessing to hyperparameter tuning. This can make LLM development faster and more accessible.
- Federated Learning: Federated Learning is a privacy-preserving approach to LLM training that allows data to be trained on locally without it leaving the device. This has the potential to improve privacy and data ownership while also reducing the amount of data required for training.
- Few-Shot and Zero-Shot Learning: These techniques aim to train models with limited or no data, which can be beneficial in low-resource settings.
- Multimodal Learning: Multimodal Learning involves training LLMs to understand different types of data, such as text, images, and audio. This can be useful for developing more sophisticated and diverse applications.
- However, with new advancements come new challenges. Some upcoming challenges in LLM Ops include:
- Model Bias: Bias in LLM models can occur due to various factors such as biased training data or biased model architecture. This can lead to unintended consequences and unfair outcomes.
- Model Interpretability: As LLM models become more complex, understanding how they make decisions can be a challenge. Model interpretability techniques are crucial for ensuring that LLM models can be understood and trusted.
- Security and Privacy: As LLM models become more valuable, ensuring their security and privacy becomes more critical. This includes securing LLM models and data, managing access to LLM models, and auditing LLM usage.
- Preparing for the future of LLM Ops requires keeping up with emerging trends and technologies while also addressing upcoming challenges. Investing in research and development, adopting new techniques and tools, and ensuring ethical and fair use of LLM models are all essential for staying ahead in the field.
Data Management for LLMs
- Data is the backbone of LLM development, and managing it effectively is critical for developing accurate and reliable LLM models. Some key considerations for data management in LLM Ops include:
- Preparing and Cleaning Data: Preparing and cleaning data involves transforming raw data into a format that can be used for LLM training and inference. This includes tasks such as data normalization, feature engineering, and data augmentation.
- Ensuring Data Quality and Consistency: Ensuring that data is of high quality and consistent is crucial for developing accurate LLM models. This involves data validation and quality control measures, such as outlier detection and data profiling.
- Managing Data Privacy and Compliance: Data privacy and compliance are essential considerations when working with sensitive or personal data. This includes implementing data security measures, such as encryption and access controls, and adhering to data privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA.
- Effective data management requires collaboration between data scientists, engineers, and stakeholders to ensure that data is clean, reliable, and ethically sourced. Investing in data management tools and processes can help to streamline data preparation and validation tasks and improve the quality of LLM models.
- LLMs are typically computationally expensive, so optimizing their performance is critical to ensure that they can be used effectively in real-world applications. Here are some key strategies for optimizing the performance of LLMs:
- Optimizing LLM inference time: One of the primary factors that affects LLM performance is the inference time required to process inputs and generate outputs. There are many techniques for optimizing inference time, including pruning unused neurons, reducing precision, and using efficient hardware accelerators.
- Using caching and memoization techniques for LLMs: Caching and memoization can help reduce the amount of computation required during LLM inference by storing the results of previous computations and reusing them when possible. This can be particularly effective for LLMs that process inputs with a high degree of overlap.
- Balancing accuracy and speed trade-offs for LLMs: In some cases, it may be necessary to sacrifice some level of accuracy in order to achieve faster inference times. It’s important to carefully consider the trade-offs between accuracy and speed when optimizing LLM performance.
Debugging and Troubleshooting LLMs
- Debugging and troubleshooting LLMs is an essential part of the LLM development process. Here are some strategies for identifying and resolving common errors in LLMs:
- Identifying and resolving common errors in LLMs: Common errors in LLMs can include issues with the input data, problems with the model architecture, and bugs in the code. Careful testing and debugging can help identify and resolve these issues.
- Debugging LLM training and inference issues: Debugging LLM training and inference issues can be challenging, as these issues may be related to the data, the model architecture, or the optimization process. It’s important to carefully monitor the training process and use diagnostic tools to identify issues as they arise.
- Developing robust LLM testing strategies: Testing is critical to ensuring the reliability and accuracy of LLMs. Robust testing strategies should include both unit tests and integration tests, as well as comprehensive validation of input and output data.
Collaboration and Communication in LLM Ops
- Effective collaboration and communication are key to successful LLM Ops. Here are some strategies for promoting collaboration and communication in LLM Ops:
- Facilitating collaboration between data scientists, engineers, and stakeholders: Collaboration between different teams and stakeholders is critical to ensuring that LLMs are developed and deployed effectively. Tools like version control, code review, and issue tracking can help facilitate collaboration.
- Communicating LLM performance and results effectively to non-technical audiences: It’s important to communicate the results of LLMs to non-technical audiences in a way that is accessible and understandable. This may require the use of visualizations, summaries, or other tools to help convey complex information.
- Promoting a culture of experimentation and continuous improvement in LLM Ops: LLM Ops is an evolving field, and it’s important to embrace a culture of experimentation and continuous improvement. This can involve trying new techniques, testing new ideas, and soliciting feedback from stakeholders.
Ethics and Fairness in LLM Ops
- LLM models have the potential to impact people’s lives significantly. Therefore, ensuring their ethical and fair use is crucial.
- Ensuring LLM models are fair and unbiased: LLM models’ fairness and accuracy are essential for their effective use. Bias can creep into LLM models due to various factors, such as biased training data or an inappropriate choice of features. It is essential to conduct regular audits of LLM models to identify and mitigate bias.
- Mitigating the risk of unintentional harm from LLM models: LLM models have the potential to cause unintentional harm, such as privacy violations, security breaches, and negative impacts on vulnerable populations. It is essential to conduct thorough risk assessments to identify potential harms and take appropriate measures to mitigate them.
- Adhering to ethical and legal standards for LLMs: LLM models must comply with ethical and legal standards. This includes adhering to data privacy regulations, ensuring transparency in LLM models’ decision-making processes, and considering the potential impact of LLM models on society. Organizations must take a proactive approach to ensure their LLM models align with ethical and legal standards.
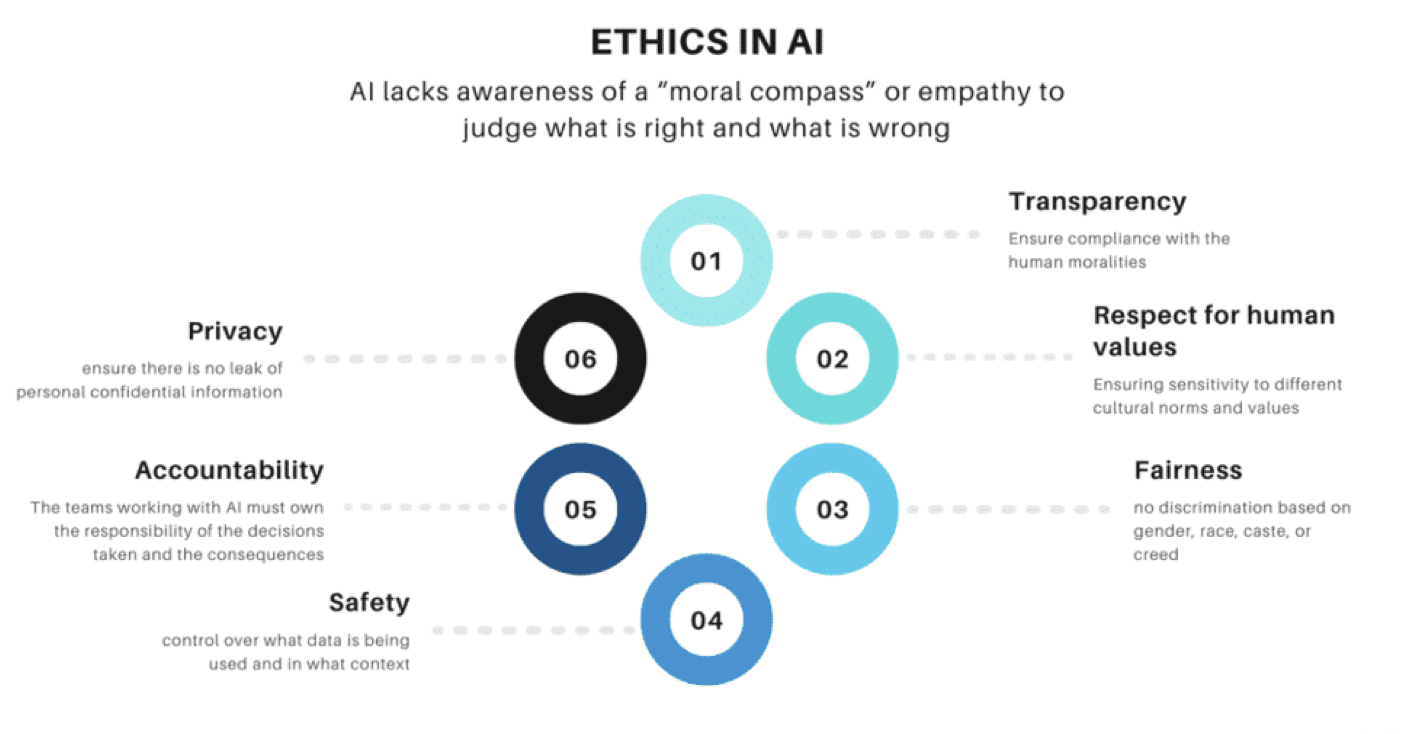
- The image below (source) details the various tenets of ethics in AI.
LLMs and Edge Computing
- As the field of artificial intelligence continues to advance, the need for real-time decision making and inference at the edge of networks has become increasingly important. This has led to the emergence of edge computing, which refers to the practice of processing data on devices located at the edge of a network, rather than in a centralized data center.
- LLMs have the potential to be highly beneficial for edge computing, as they are able to process natural language inputs in real-time and generate accurate responses quickly. However, deploying LLM models on edge devices presents several challenges that must be addressed.
- Deploying LLM models on edge devices: To deploy an LLM model on an edge device, it must first be optimized to run efficiently on a device with limited computing resources. This involves reducing the size of the model and minimizing its memory and processing requirements. Once the model has been optimized, it can be deployed on the edge device.
- Challenges and solutions for running LLMs on edge computing devices: One of the main challenges of running LLMs on edge devices is the limited computing resources available on these devices. LLM models are typically very large and require significant amounts of memory and processing power to run. To overcome this challenge, techniques such as model compression, quantization, and pruning can be used to reduce the size of the model and make it more efficient.
- Another challenge is the need to maintain data privacy and security while running LLMs on edge devices. This can be addressed through techniques such as federated learning, which allows models to be trained on edge devices without exposing sensitive data.
- Use cases and benefits of LLMs on edge devices in industries such as IoT and robotics: There are many potential use cases for LLMs on edge devices, particularly in industries such as IoT and robotics. For example, LLMs could be used to process natural language inputs in real-time and generate responses on devices such as smart speakers, chatbots, and voice assistants.
- In the field of robotics, LLMs could be used to enable robots to understand and respond to natural language inputs in real-time, making them more responsive and easier to interact with. LLMs could also be used in IoT devices to enable real-time natural language processing of sensor data, making it easier to monitor and control devices in real-time.
- Overall, the deployment of LLM models on edge devices presents both challenges and opportunities. By optimizing LLM models for edge computing and addressing issues such as data privacy and security, it is possible to unlock the potential of LLMs in industries such as IoT and robotics, and enable real-time natural language processing at the edge of networks.
Takeaway
- LLMs offer tremendous potential for improving a wide range of applications, but also present unique challenges for MLOps engineers. By addressing key areas such as data management, model training and tuning, deployment, interpretation, testing, security, CI/CD, monitoring and logging, and governance and compliance, MLOps engineers can ensure the reliability, security, and performance of LLMs in production environments.
- LLMs have revolutionized the field of AI, and LLM Ops is a crucial aspect of ensuring that these models are developed, deployed, and managed effectively. With the increasing adoption of LLMs in various industries, it’s crucial to stay up to date with the latest advancements and best practices in LLM Ops to ensure that these models deliver accurate and reliable results while adhering to ethical and legal standards.





