CS230 • Deep Learning Intro and Applications
What is Deep Learning?
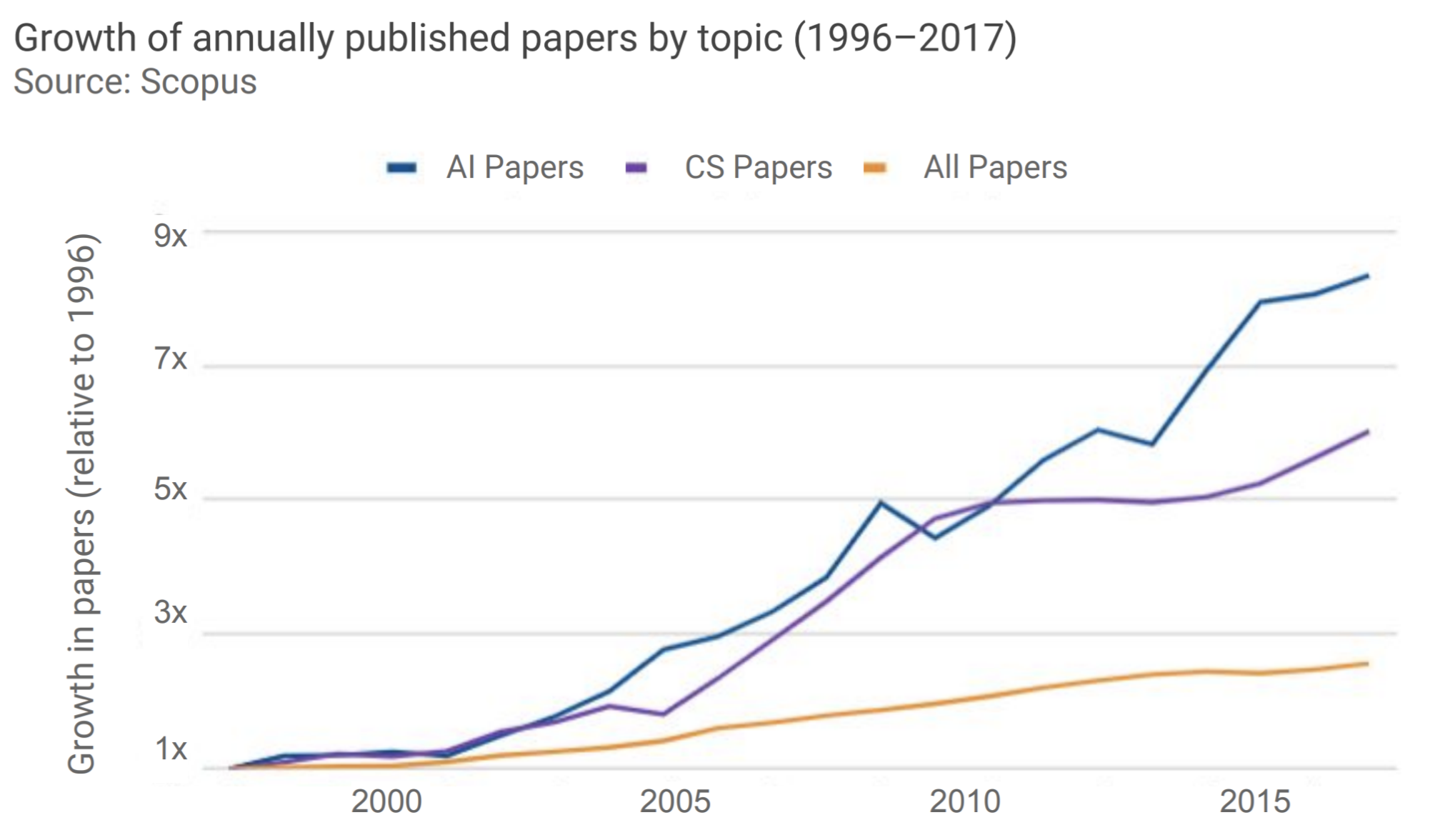
- The growth in annually published papers in AI has outpaced that of CS. This means that there is a growing number of AI publications by researchers from other scientific fields (Physics, Chemistry, Astronomy, Material Science, etc.).
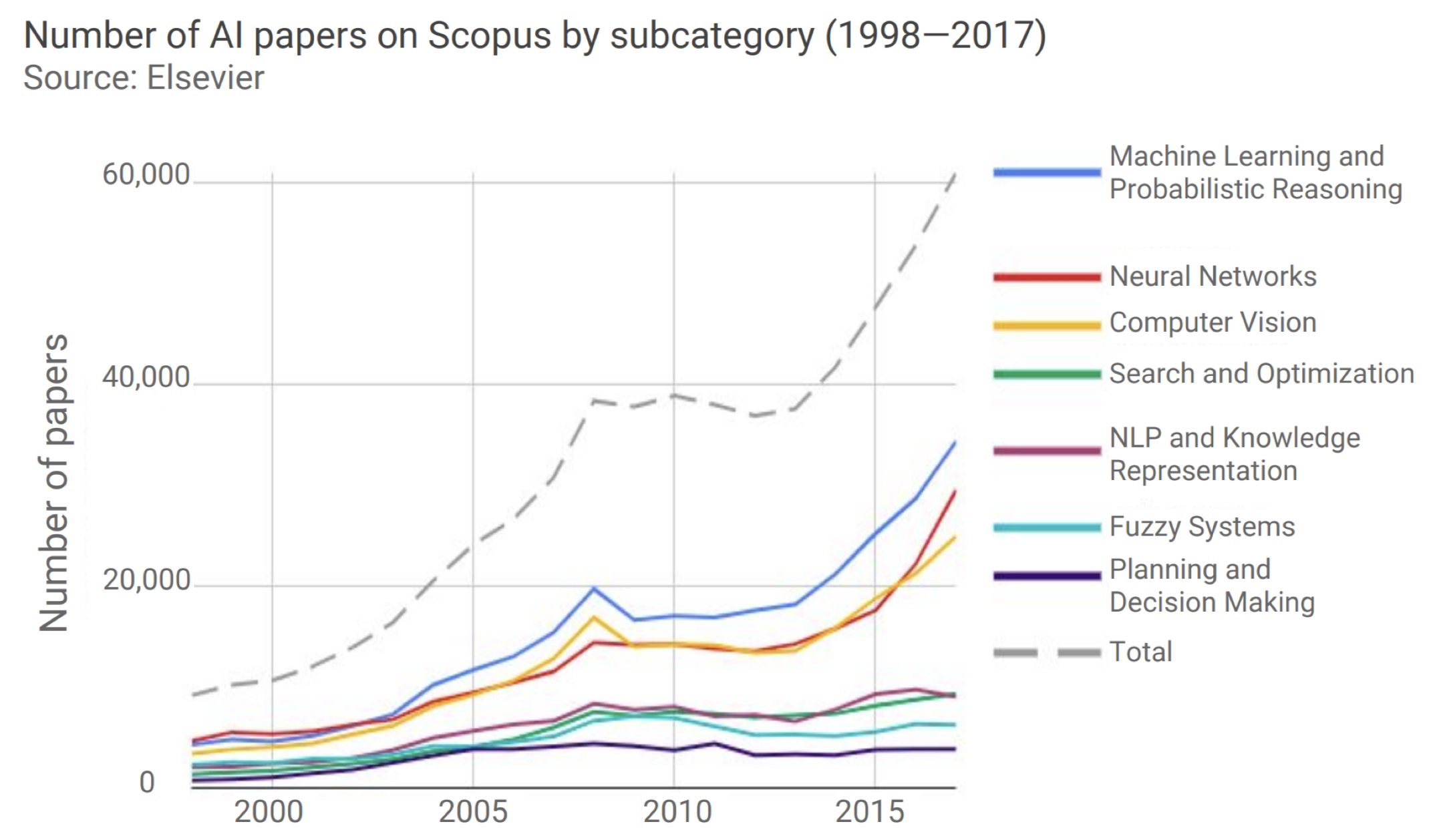
- Every year, 2/3 of the students of this course are not majoring in CS. Many CS 230 projects are a combination of computer science and other domains that students have expertise with. The number of papers published with the keyword “Neural Network” has been rapidly growing.
-
The number of Scopus papers on Neural Networks had a compound annual growth rate of 37% from 2014 to 2017. It has notably driven the growth of papers published In Machine Learning and Computer Vision. When we talk about Neural Networks we are talking about Deep Learning. Deep Learning is a subclass of Machine Learning, and Machine Learning is again a subclass of Artificial Intelligence. Deep learning has reshaped the research frontier of Machine Learning, Computer Vision, as well as Natural Language Processing. We’ve seen that Deep Learning/Machine Learning has already invaded our lives with lots of industrial products, for example, conversational assistants. Today cell phones are unlocked through face verification, which is another application powered by Deep Learning. Other applications are: Self-Driving - more especially Perception which aims at giving cars the ability to detect pedestrians and traffic signs - Itinerary, Mapping, Sentiment Analysis, Machine Translation.
-
Digitalization, computational power and the evolution of algorithms have allowed AI to boom. Machine Learning is all about trying to mimic a function mapping data to labels and use this function to make predictions of labels for new data afterwards. The way we use hardware to track all kinds of data we encountered in our daily life provide a giant database that the algorithms can take advantage from. Computational power is important because the mimicing process is all about iteratively doing large matrix multiplication. Unlike linear regression that only fits a line in high dimension space to the given data, Deep Learning is scalable to large data. That is to say, having a large number of data isn’t going to help linear regression pretty well, because it doesn’t have the ability the understand that large amount of data. Deep Learning, on the other hand, isn’t the case.
Introduction to Deep Learning Applications
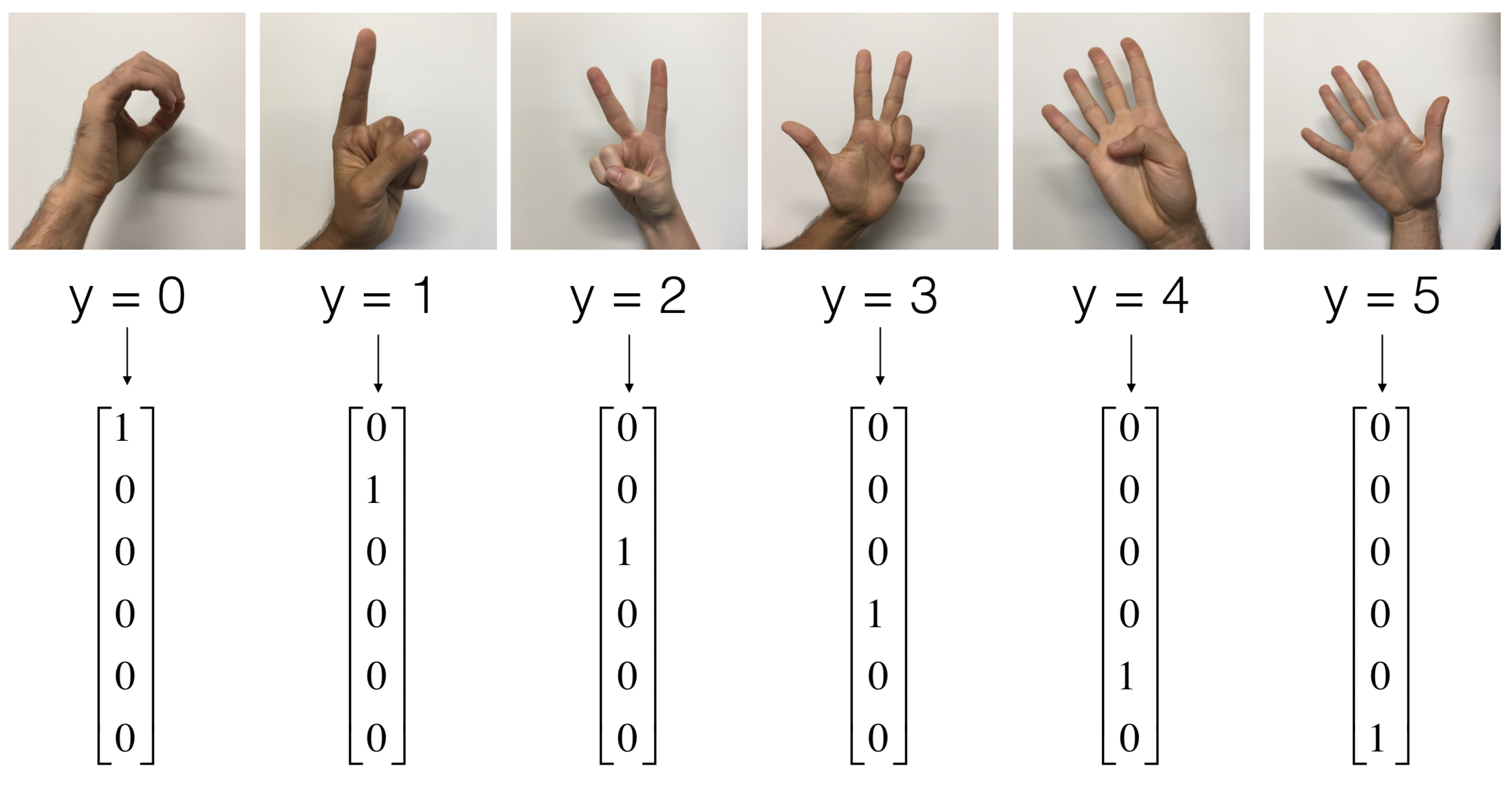
1) SIGN language detection
- Taking an input image of a hand which has a number (between 0 and 5) in sign language and predicting the number that the hand corresponds to. Problem highly correlated to sign translation.
2) The Happy House
- A house letting in smiling people only. An application part of sentiment analysis on an image.
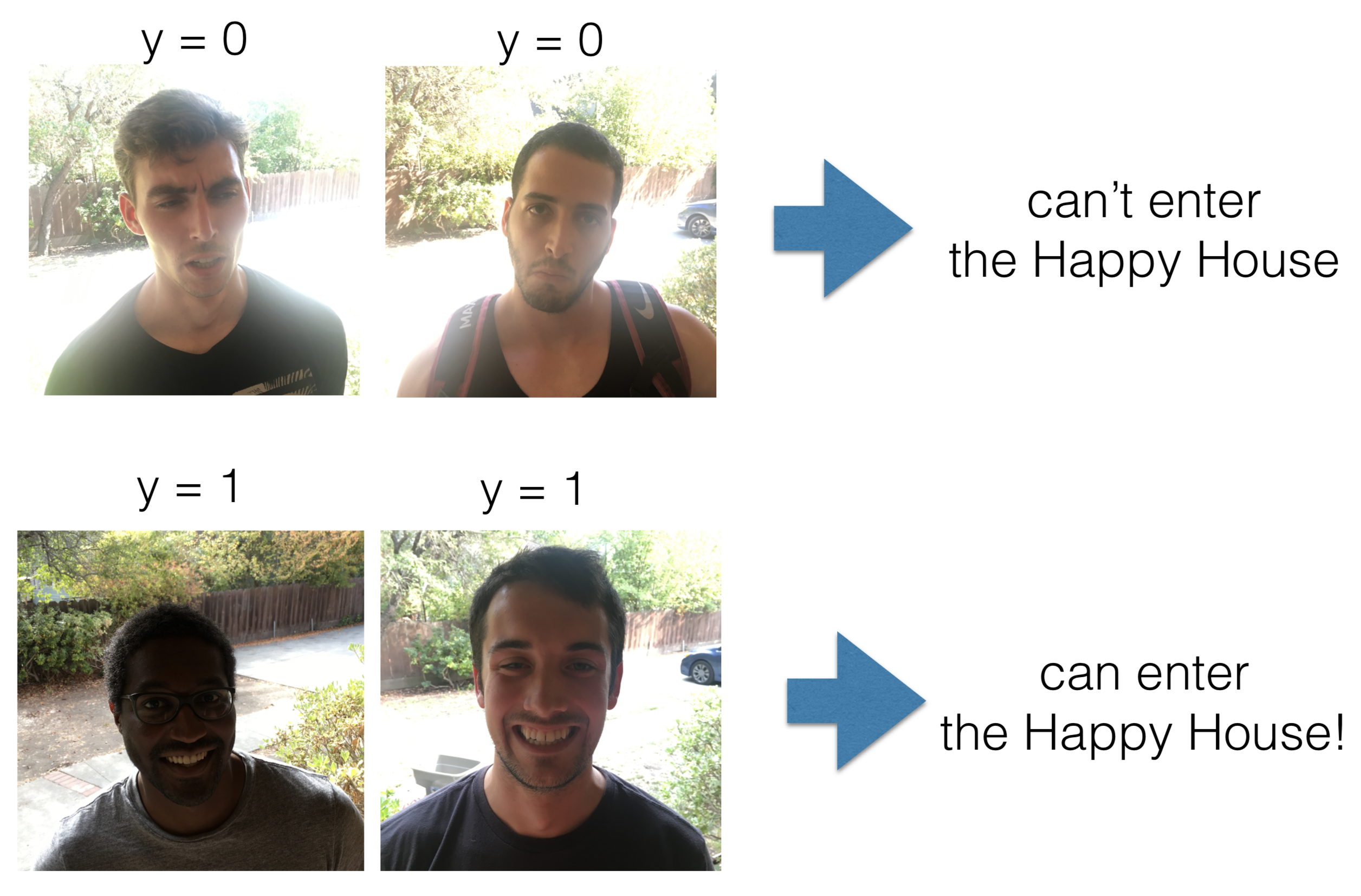
- Other related tasks are Face Verification or Face Recognition.
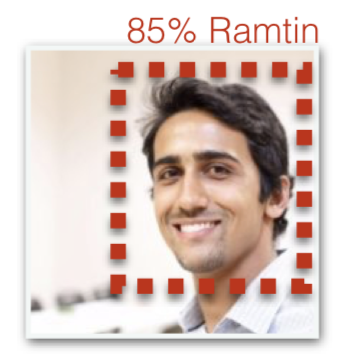
3) Face Recognition
- Given an image of a person, prediction of their identity.
4) Object Detection
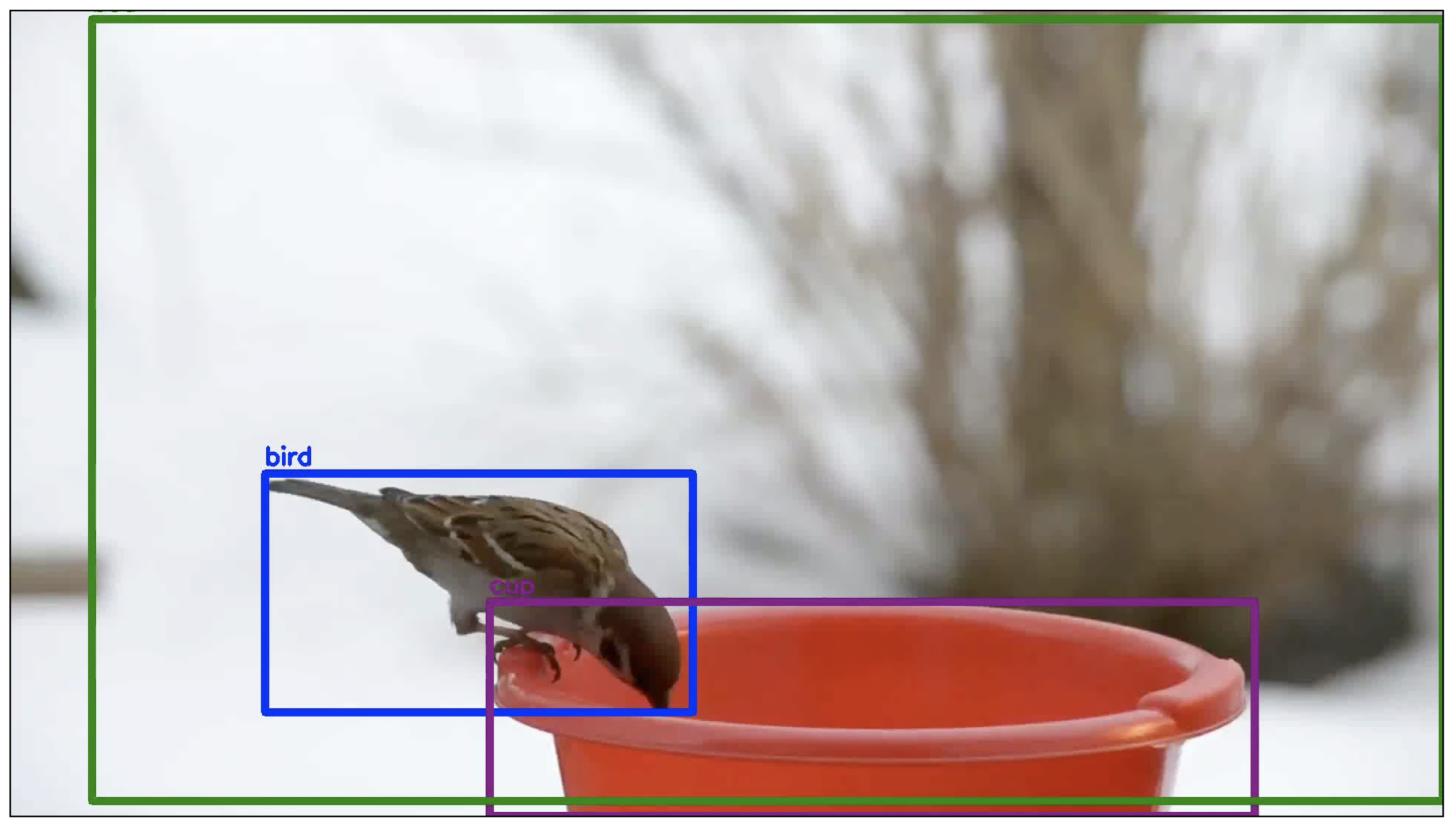
- For example, car detection for autonomous driving using YOLOv2.

5) Optimal goalkeeper shoot prediction
- Determining the geographical location a player should kick a ball from to increase the chances to give it to one of their teammates.

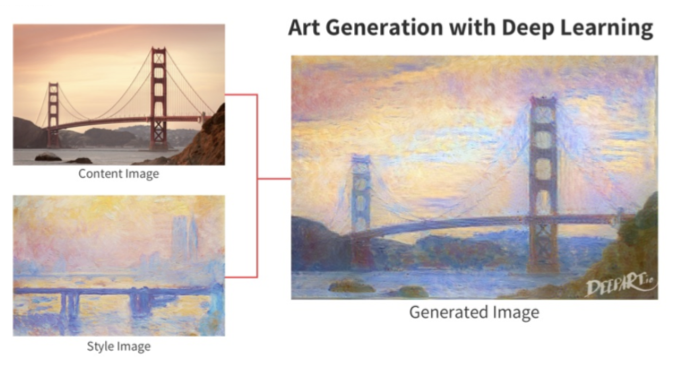
6) Art Generation
- Generation of a content image as if it was painted with the style of another image.
7) Music Generation using a sequence model

8) Text Generation
- Given a large corpus of Shakespeare poems, producing a poem as if it was written by Shakespeare.

9) Sentiment analysis
- Based on the sentence, producing the emoji which represents this sentence. Task related to how smartphones are able to suggest emoji or a next word given a specific word.
10) Machine Translation
- One of the major applications of Deep Learning.

11) Trigger word detection
- Building an algorithm which activates itself when the word “activate” is pronounced. Related to the functioning of Siri, Alexa, Cortana.

Examples of student projects
1) Coloring Black&White pictures with Deep Learning
- To train such an algorithm, we would need colored images and their gray-scale versions to build the mapping between colored and gray-scale images.

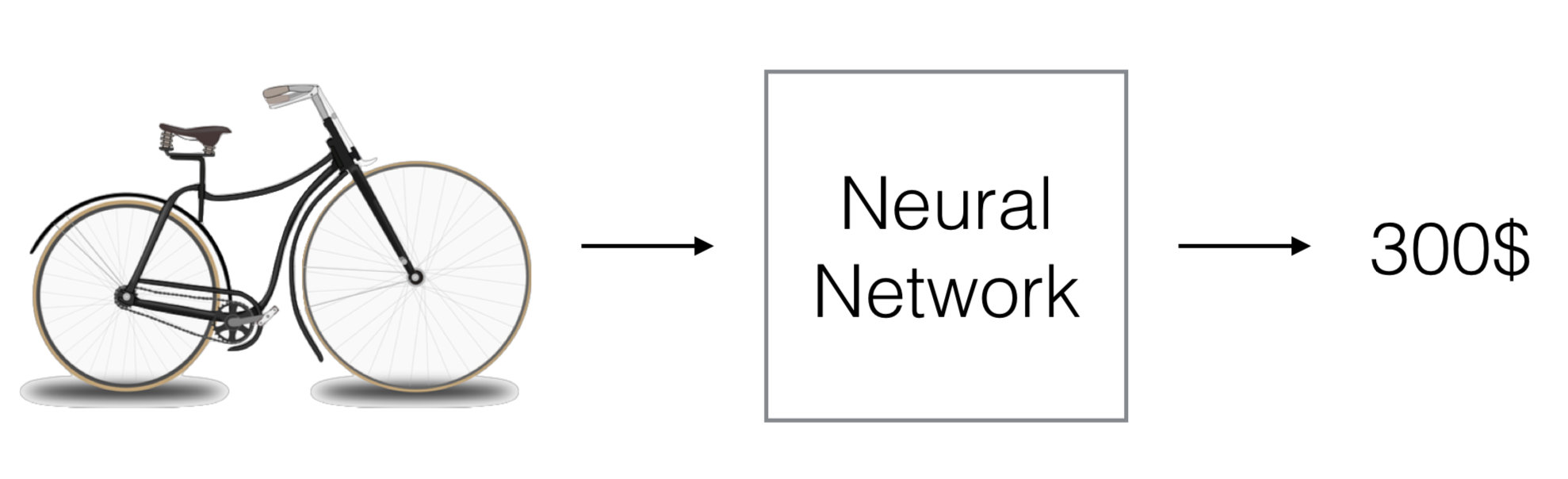
2) Predicting a price of an object from a picture
- Students implemented a feature showing which parts of the bike were discriminative for the price of the bike.
- The algorithm was really efficient at predicting the price of kids’ bikes because it was looking at the back to see that there was an additional wheel. It was trained with data of kids’ bikes to be able to learn this pattern.
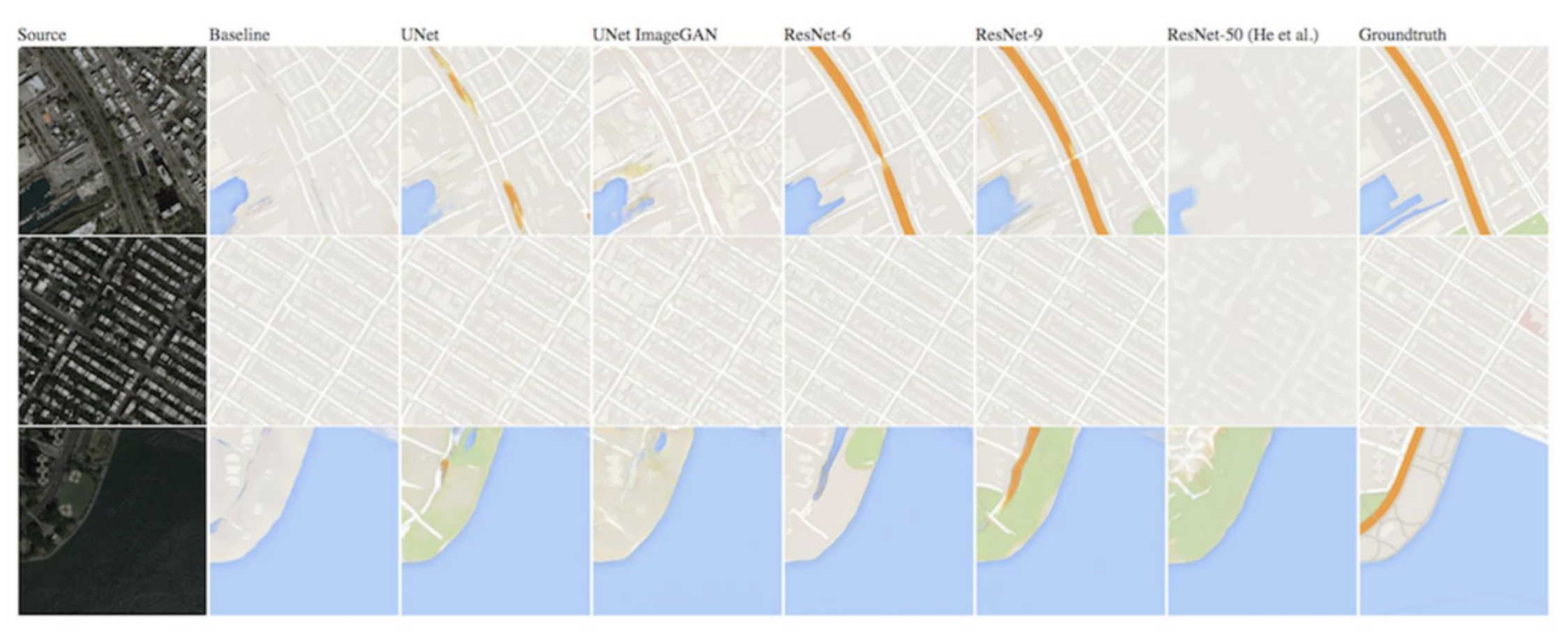
3) Image-to-Image translation with Conditional GAN
- The algorithm generates a map from an input satellite image.
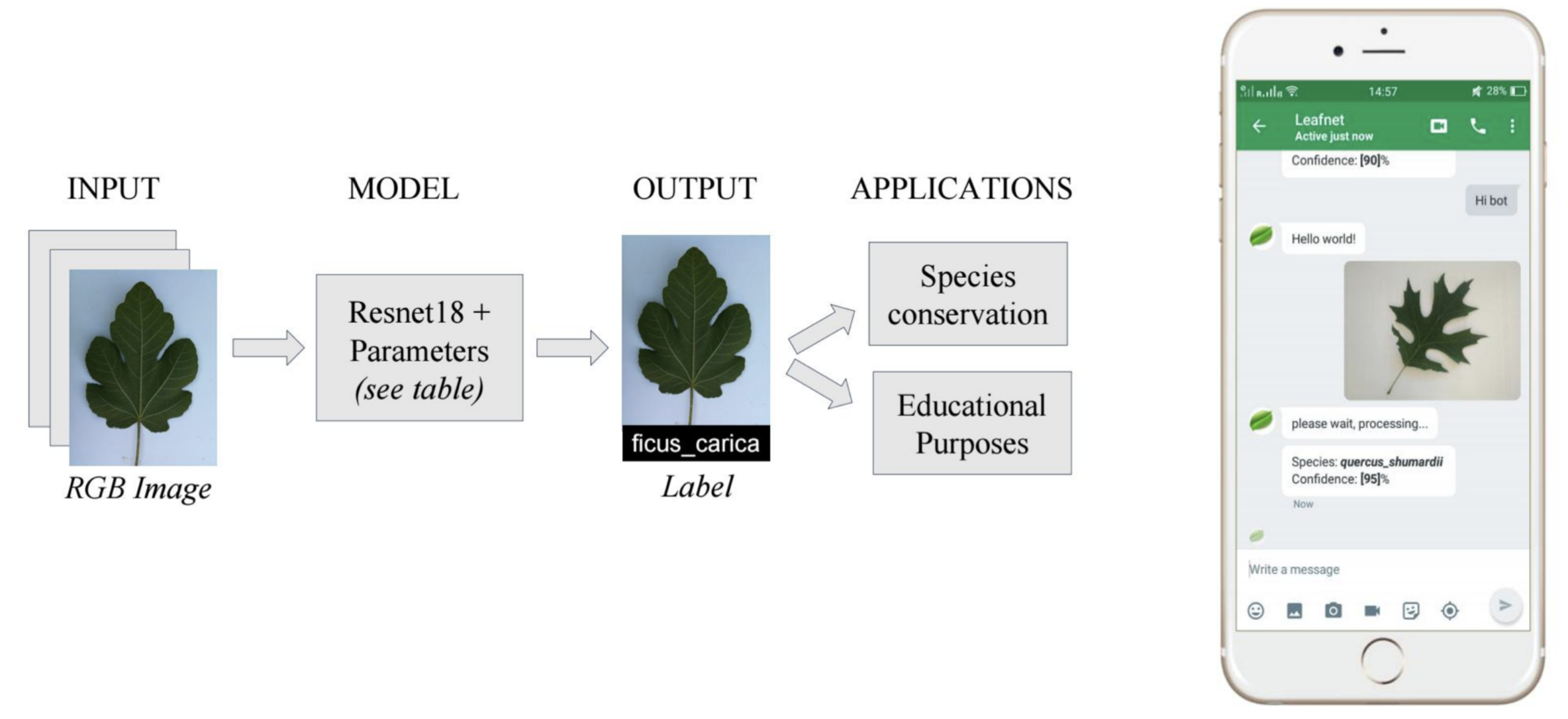
4)LeafNet: A Deep Learning Solution to Tree Species identification
- Students built an application able to predict a tree species from a taken photograph of a leaf.